专栏原创出处:github-源笔记文件 (opens new window) ,github-源码 (opens new window),欢迎 Star,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。 本节内容对应官方文档 (opens new window),本节内容对应示例源码 (opens new window)
# 1 窗口函数概念
窗口函数为每个窗口上执行计算。一旦确定某个窗口已准备好进行处理,就可以使用该窗口函数来处理每个(可能是 Keyed Windows)窗口的元素
窗口机制(```scala:Flink DataStream 窗口机制)
分析WindowedStream源码提供方法:
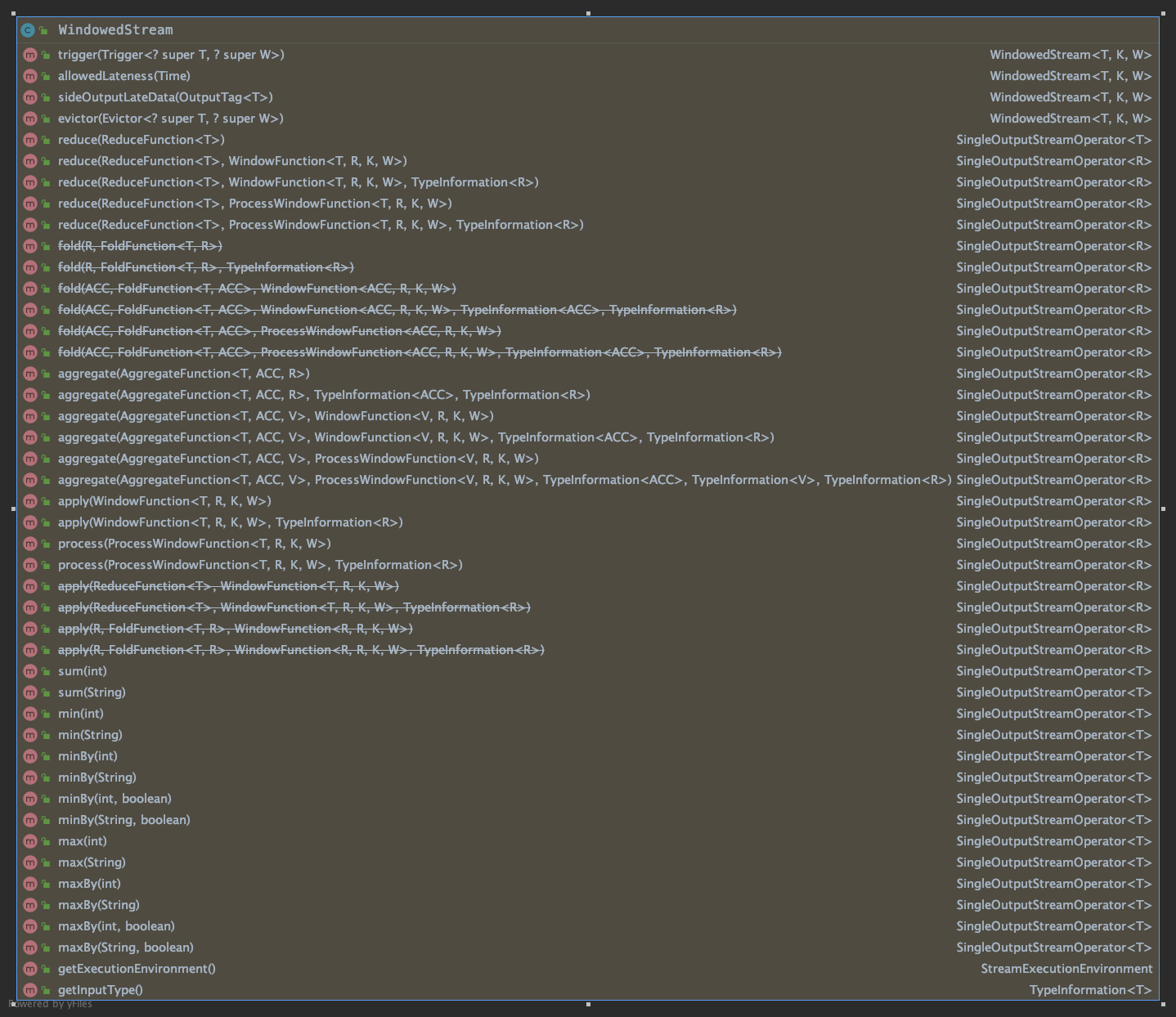
支持的窗口函数主要为:
- WindowFunction
- ProcessWindowFunction
- ReduceFunction
- AggregateFunction
- FoldFunction 分别对应函数为.reduce/aggregate/fold/apply() 中需要做的操作。
废弃说明:fold、apply 已废弃推荐使用 aggregate 函数,废弃的函数不进行文档说明
# 1.1 WindowFunction 与 ProcessWindowFunction 区别
分析提供方法,对于各类型函数提供了 WindowFunction 与 ProcessWindowFunction 方法,使用 reduce 相关函数分析关联关系如下:
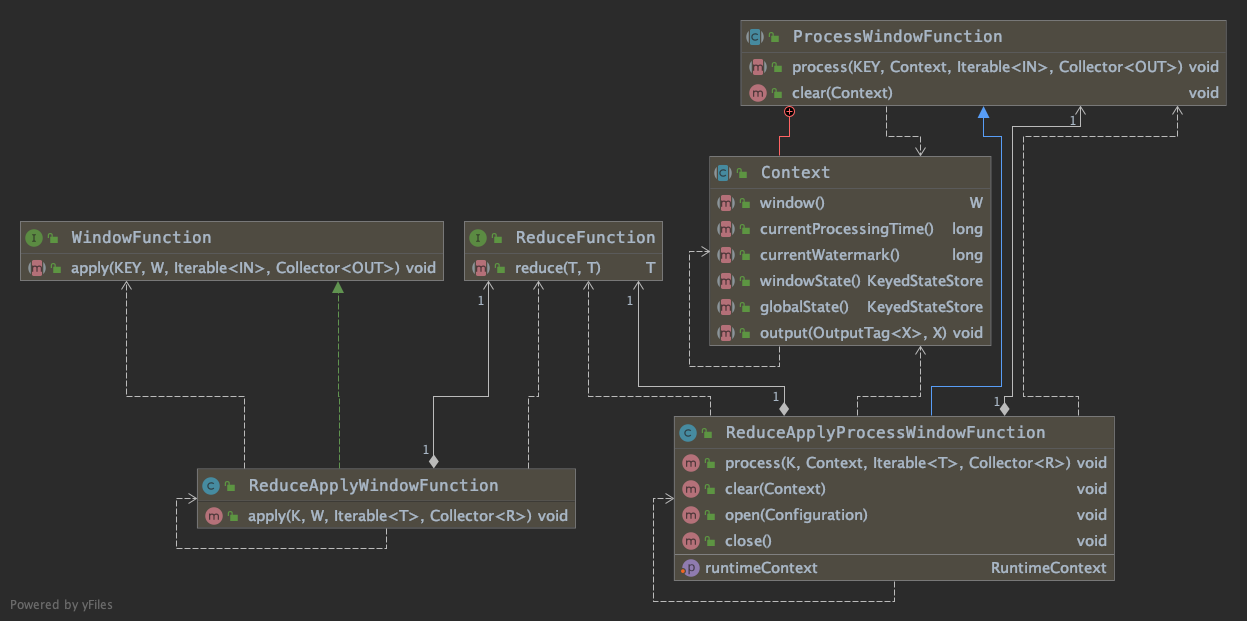
WindowFunction 处理方法: void apply(KEY key, W window, Iterable<IN> input, Collector<OUT> out) ProcessWindowFunction 处理方法: void process(KEY key, Context context, Iterable<IN> elements, Collector<OUT> out)
区别点主要为:WindowFunction 可以访问当前窗口,ProcessWindowFunction 可以访问当前 Context
# 1.2 ProcessWindowFunction
该函数获取一个 Iterable,该 Iterable 包含窗口的所有元素,以及一个 Context 对象,该对象可以访问时间和状态信息,从而使其比其他窗口函数更具灵活性 这是以性能和资源消耗为代价的,因为无法增量聚合元素,而是需要在内部对其进行缓冲,直到将窗口数据全部准备好进行处理为止。
使用每个窗口状态
调用在 Context 对象上 process() 有两种方法可以访问两种状态:
- globalState(),它允许访问不在窗口范围内的键状态
- windowState(),它允许访问也作用于窗口的键控状态
如果您预期同一窗口会多次触发,则此功能很有用,例如,对于迟到的数据有较早的触发,或者您有进行推测性较早触发的自定义触发器时。在这种情况下,您将存储有关先前触发或每个窗口状态中触发次数的信息。
使用窗口状态时,清除窗口时也要在 clear() 方法中清除该状态
注意
该 key 参数是通过提取的关键 KeySelector 是被指定的 keyBy() 调用。
如果是元组索引键或字符串字段引用,则始终使用此键类型,Tuple 并且必须手动将其强制转换为正确大小的元组以提取键字段。
性能说明
ProcessWindowFunction 用于简单的聚合(如 count)效率很低。
具有增量聚合的窗口函数 部分说明如何将 ReduceFunction 或 AggregateFunction 与或结合使用,
以ProcessWindowFunction同时获得增量聚合和的附加信息ProcessWindowFunction。
示例代码:
object ApplyProcessWindowFunction extends WindowedStreamFunctions {
window
.process(new MyProcessWindowFunction())
.print()
sEnv.execute(this.getClass.getName)
class MyProcessWindowFunction
extends ProcessWindowFunction[(String, Double), String, Tuple, TimeWindow] {
override def process(key: Tuple,
context: Context,
elements: Iterable[(String, Double)],
out: Collector[String]): Unit = {
var count = 0L
for (_ <- elements) {
count = count + 1
}
out.collect(s"Window ${context.window} count: $count")
}
}
}
# 1.3 WindowFunction
使用 WindowFunction 函数
参考 ApplyProcessWindowFunction 中 ProcessWindowFunction 用法,相对于 ProcessWindowFunction,WindowFunction 不可访问 context 内容
示例代码:
object ApplyWindowFunction extends WindowedStreamFunctions {
window
.apply(new MyWindowFunction())
.print()
sEnv.execute(this.getClass.getName)
class MyWindowFunction
extends WindowFunction[(String, Double), String, Tuple, TimeWindow] {
override def apply(key: Tuple,
window: TimeWindow,
input: Iterable[(String, Double)],
out: Collector[String]): Unit = {
var count = 0L
for (_ <- input) {
count = count + 1
}
out.collect(s"Window ${window} count: $count")
}
}
}
# 1.4 reduce
将输入中的两个元素组合在一起以产生相同类型的输出元素
object ApplyReduce extends WindowedStreamFunctions {
window
.reduce((o1, o2) => o1.copy(_2 = o1._2 + o2._2))
.print()
sEnv.execute(this.getClass.getName)
}
# 1.5 aggregate
Flink 的AggregateFunction是一个基于中间计算结果状态进行增量计算的函数。
由于是迭代计算方式,所以,在窗口处理过程中,不用缓存整个窗口的数据,所以效率执行比较高。
AggregateFunction 泛型说明 输入类型(IN),迭代数据类型(ACC),和一个输出类型(OUT)
AggregateFunction 方法说明
- ACC createAccumulator(); 迭代状态的初始值
- ACC add(IN value, ACC accumulator); 每一条输入数据,和迭代数据如何迭代
- ACC merge(ACC a, ACC b); 多个分区的迭代数据如何合并
- OUT getResult(ACC accumulator); 返回数据,对最终的迭代数据如何处理,并返回结果。
示例代码:
object ApplyAggregate extends WindowedStreamFunctions {
window
.aggregate(new AverageAggregate())
.print()
sEnv.execute(this.getClass.getName)
/*
执行解释:
1.给定迭代初始值 (0, 0)。 元组 第一个记录分数,第二个记录数据条数
2.输入的数据,获取分数,累加到迭代值元组的第一个元素中,迭代值元组的第二个值记录条数加 1 。
3.每一个分区迭代完毕后,各分区的迭代值合并成最终的迭代值
4.对最终的迭代处理,获取最终的输出结果。
*/
class AverageAggregate extends AggregateFunction[(String, Double), (Double, Double), Double] {
// 迭代的初始值
override def createAccumulator(): (Double, Double) = (0L, 0L)
// 每一个数据如何和迭代数据 迭代
override def add(value: (String, Double), accumulator: (Double, Double)): (Double, Double) =
(accumulator._1 + value._2, accumulator._2 + 1L)
// 返回结果
override def getResult(accumulator: (Double, Double)): Double =
accumulator._1 / accumulator._2
// 每个分区数据之间如何合并数据
override def merge(a: (Double, Double), b: (Double, Double)): (Double, Double) =
(a._1 + b._1, a._2 + b._2)
}
}
# 2 具有增量聚合的窗口函数
增量聚合函数,支持组合 (预处理函数+窗口函数)
- pre-Function[T] + ProcessWindowFunction[T, R, K, W]
- pre-Function[T] + WindowFunction[T, R, K, W]
增量聚合函数由于是基于中间状态计算,因此性能较好,但是灵活性却不及 ProcessWindowFunction
缺失了对窗口状态数据的操作以及对窗口中元数据信息的获取等。但是使用全量聚合函数去完成一些基础的增量统计运算又相对比较浪费资源,性能低于增量。
因此 Flink 提供了一种方式,可以将 Incremental Aggregation Function 和 ProcessWindowFunction 整合起来,
充分利用这两种计算方式的优势去处理数据。
本示例为:具有 ReduceFunction 的增量窗口聚合
// 本示例调用使用 WindowedStream 类中 reduce 函数如下
def reduce[R: TypeInformation](
preAggregator: (T, T) => T,
function: ProcessWindowFunction[T, R, K, W]): DataStream[R]
object ApplyIncrementalReduce extends WindowedStreamFunctions {
window
.reduce(
(r1: (String, Double), r2: (String, Double)) => r1._1 -> (r1._2 + r2._2),
new ProcessWindowFunction[(String, Double), (Long, (String, Double)), Tuple, TimeWindow] {
override def process(key: Tuple,
context: Context,
elements: Iterable[(String, Double)],
out: Collector[(Long, (String, Double))]): Unit = {
val min = elements.iterator.next()
out.collect((context.window.getStart, min))
}
}
)
.print()
sEnv.execute(this.getClass.getName)
}